PPM ↔ mS/cm Calculator
Convert between Total Dissolved Solids (PPM) and Electrical Conductivity (mS/cm).
The factor depends on ionic composition. 640 is a common default.
1 mS/cm = 1000 µS/cm (Microsiemens per centimeter)
PPM to Millisiemens Calculator – Convert PPM to mS/cm Instantly
Understanding water quality is a crucial task in many fields, from gardening and hydroponics to aquariums and industrial processes. When you’re measuring the dissolved minerals and salts in water, you often encounter two key terms: PPM (Parts Per Million) and Millisiemens (mS/cm). While they both tell you something about the water’s purity, they measure it in different ways.
Our PPM to Millisiemens calculator is a simple tool designed to help you quickly and accurately convert between these two measurements, giving you a clearer picture of your water’s quality.
How to Use the PPM to Millisiemens Calculator
Using the calculator is straightforward, even if you’re new to these concepts. Follow these simple steps to get an instant and accurate conversion.
- Enter Your PPM Value: In the first box, titled “PPM (Parts Per Million),” enter the reading from your TDS meter. This value represents the total amount of dissolved solids in your water.
- Adjust the Conversion Factor (k-factor): The k-factor is the most important part of this conversion. It’s a specific constant that varies depending on the type of dissolved minerals in your water. Our calculator provides a slider to easily adjust this factor between 0.4 and 0.8. If you don’t know the exact factor for your water, a value between 0.5 and 0.7 is a common approximation.
- Click “Calculate”: Once you’ve entered your values, simply click the “Calculate” button. The result will instantly appear in the “Converted Value (EC)” section below.
That’s it! In a few seconds, you’ll have your water’s total dissolved solids (TDS) converted to its electrical conductivity (EC).
Formula & Conversion Explanation
To truly understand what the PPM to Millisiemens calculator is doing, it’s helpful to know the science behind the conversion.
What is PPM (Parts Per Million)?
PPM, or parts per million, is a unit of concentration. It tells you how many “parts” of a substance are present in one million parts of a solution. In the context of water quality, PPM measures TDS (Total Dissolved Solids)—the total weight of all inorganic and organic substances dissolved in a given volume of water. Think of it as a direct measure of the “stuff” in your water.
What are Millisiemens (mS/cm)?
Millisiemens per centimeter (mS/cm) is a unit of measurement for Electrical Conductivity (EC). Water that is completely pure (like distilled water) is a very poor conductor of electricity. However, when minerals, salts, and other dissolved solids are present, they become ions that can conduct an electrical current. The more dissolved solids in the water, the higher its conductivity. EC, therefore, is an indirect measurement of the concentration of these dissolved ions.
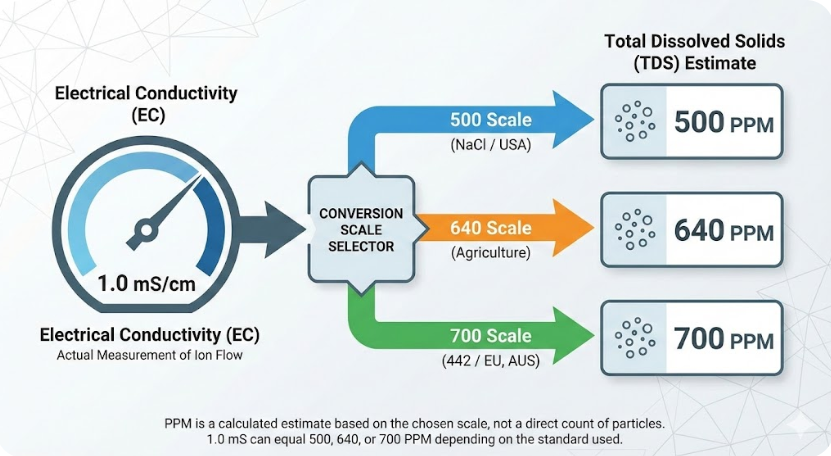
The Conversion Formula & The k-factor
The relationship between PPM (TDS) and Millisiemens (EC) isn’t a fixed, one-to-one ratio. It is an approximation based on a conversion factor, or k-factor, which accounts for the specific mineral composition of the water. The formula is:
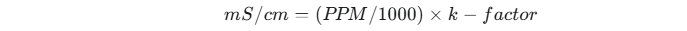
As you can see, a value of 1000 is used to convert PPM into parts per thousand, which then gets multiplied by the k-factor. The k-factor is crucial because different ions conduct electricity at different rates. For instance, the conversion factor for sodium chloride (table salt) is different from that of a common hydroponic nutrient mix. This is why our calculator allows you to adjust the factor, giving you more control and accuracy.
Applications & Use Cases of PPM to Millisiemens
Knowing how to convert between PPM and mS/cm is not just a scientific exercise; it has practical applications across various fields. Here are some of the most common use cases:
Hydroponics and Gardening
For hydroponic growers, monitoring nutrient strength is critical for plant health. EC is the standard measurement used to ensure plants are receiving the right amount of nutrients. By converting your PPM nutrient solution to EC, you can accurately track and adjust your fertilizer levels to prevent nutrient burn or deficiency. This helps in maximizing plant growth and yield.
Aquarium and Fish Keeping
Maintaining water quality is paramount for the health of aquatic life. Both freshwater and saltwater aquariums have specific parameters for TDS and EC. Converting between these measurements helps you ensure the water is a safe and healthy environment for your fish and corals, preventing stress and disease.
Water Purification and Filtration
Whether you’re using reverse osmosis (RO), distillation, or deionization, monitoring the water before and after treatment is essential. Measuring the PPM or EC of the water helps you determine the efficiency of your filtration system and know when it’s time to replace a filter. High PPM or EC readings after filtration can indicate a problem with the system.
Agriculture and Irrigation
In large-scale farming, water quality can significantly impact crop health. High levels of salinity, measured by TDS or EC, can be detrimental to certain crops. Farmers use these measurements to determine the suitability of water sources for irrigation and to manage soil salinity, ensuring a productive harvest.
FAQs about PPM to Millisiemens Conversion
What is the difference between TDS and EC?
TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) is a measure of the total weight of all solid materials dissolved in water, typically expressed in PPM or mg/L. EC (Electrical Conductivity) is a measure of the water’s ability to conduct an electrical current, expressed in units like mS/cm. While they are related, they measure different properties. An EC meter measures conductivity, then uses an internal conversion factor to estimate the TDS value.
Why do I need a conversion factor?
The conversion factor, or k-factor, is necessary because different dissolved solids have varying effects on electrical conductivity. For example, a water sample with 500 PPM of sodium chloride will have a different EC than a sample with 500 PPM of calcium carbonate. The k-factor accounts for these differences, providing a more accurate estimation of the conversion.
What is a common k-factor to use?
A general-purpose k-factor of 0.5 is often used as a standard approximation. However, for specific applications, a k-factor between 0.64 and 0.70 is common in hydroponics, as it more closely reflects the properties of most nutrient solutions. It’s always best to use the k-factor recommended by your meter manufacturer or nutrient brand.
Can I convert mS/cm back to PPM?
Yes, you can easily convert mS/cm back to PPM by reversing the formula.
What is the ideal PPM or EC for drinking water?
The ideal levels can vary, but the EPA recommends a maximum TDS of 500 PPM for drinking water. Water with very low TDS (e.g., from an RO system) may be tasteless, while water with very high TDS can have an unpleasant taste and may not be suitable for drinking. Most people find drinking water with a TDS of 50-150 PPM to be very palatable.
Are there other units I should know about?
Yes, you might also encounter micro-Siemens per centimeter (μS/cm). There are 1000 micro-Siemens in 1 milli-Siemens, so a simple conversion is to multiply your mS/cm value by 1000 to get μS/cm.
Why is EC considered a “truer” measurement than PPM?
EC is a direct electrical measurement of the water’s conductivity. PPM, on the other hand, is an estimated value that’s derived from the EC reading using a conversion factor. This is why most professional water testing applications rely on EC as the primary metric, as it provides a more consistent and repeatable result regardless of the specific meter or conversion scale being used.
