Molarity to PPM Calculator
Formula:
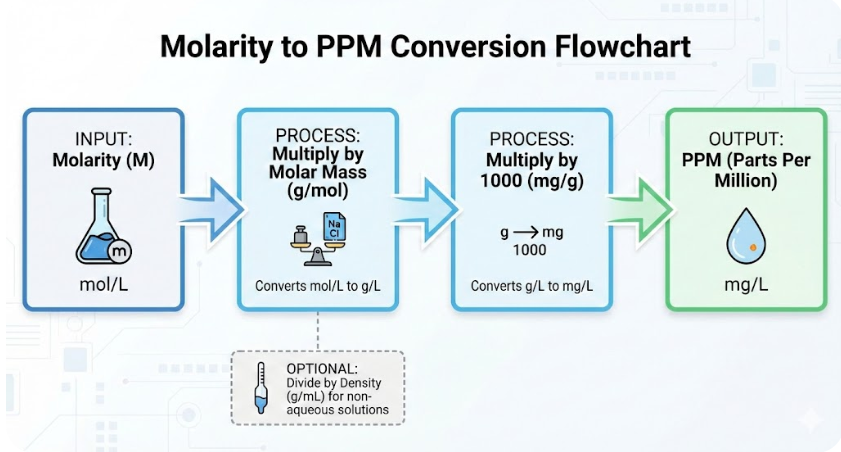
PPM = Molarity × Molar Mass × 1000
Where:
• Molarity = mol/L
• Molar Mass = g/mol
• 1 g/L = 1000 mg/L = 1000 PPM (for dilute aqueous solutions)
M to PPM Calculator – Accurate Molarity to PPM Conversion Tool
Easily convert molarity (M) to PPM using molecular weight, volume, and solution concentration. Ideal for chemistry labs, environmental testing, pharmaceuticals, and analytical calculations.
The Molarity to PPM Calculator is a simple, fast tool designed for students, lab technicians, and hobbyists who need to convert chemical concentrations. It takes the guesswork out of converting between molarity (moles per liter) and parts per million (PPM), a common challenge in chemistry, environmental science, and hydroponics.
If you’ve ever asked, “How do I convert my fertilizer’s molar concentration to PPM?” or “What’s the PPM of a 0.1 M NaCl solution?”, this calculator provides a quick, accurate answer.
How to Calculate Molarity to PPM
To use the calculator, you’ll need three key pieces of information:
- Molarity (M): The number of moles of solute per liter of solution. For example, a 0.5 M solution.
- Molar Mass (g/mol): The mass of one mole of the substance. You can find this on a periodic table or by adding up the atomic masses of the elements in your compound (e.g., NaCl has a molar mass of 58.44 g/mol).
- Solution Density (g/mL): The mass of the solution per unit volume. For most dilute aqueous solutions, you can assume a density of 1 g/mL.
The calculator automates the standard formula:
PPM=Density×1000(Molarity×MolarMass×1,000,000)
This equation gives you the concentration in milligrams of solute per kilogram of solution, which is the definition of PPM. By inputting your values, the tool handles the unit conversions and calculations instantly.
Why is this Conversion Important?
Converting molarity to PPM is essential for precision in many applications. For instance, in aquariums and hydroponic gardening, nutrient levels are almost always measured in PPM. If you’re preparing a nutrient solution from a concentrated stock (measured in Molarity), you need to convert it to ensure your plants or fish receive the correct dosage.
A small error can lead to nutrient burn or deficiencies. Similarly, in environmental analysis, reporting the concentration of a pollutant in parts per million is standard practice for clarity and consistency. This calculator provides a reliable way to bridge the gap between theoretical chemistry and real-world application, ensuring your results are consistent and accurate every time.
