Bleach PPM Calculator
Accurately calculate bleach dilutions for sanitizing and disinfecting.
Your Dilution Recipe:
Bleach to Add:
Water to Add:
Dilution Ratio:
Bleach PPM Calculator – Convert Bleach Concentration to Parts Per Million
Do you need to create a sanitizing solution for your home, a restaurant, or a daycare? Getting the right concentration is crucial—too weak, and it won't be effective; too strong, and it can be corrosive and potentially unsafe. This is where a Bleach PPM Calculator comes in. It's a simple, powerful tool that takes the guesswork out of diluting bleach, helping you create safe and effective solutions every time.
This guide is for anyone who needs to make a precise sanitizing solution, from professional food handlers to homeowners. We'll demystify the science behind bleach dilutions, explain what PPM means in a real-world context, and show you exactly how to use a calculator to get the perfect mix.
What is PPM and Why is it Essential for Bleach Solutions?
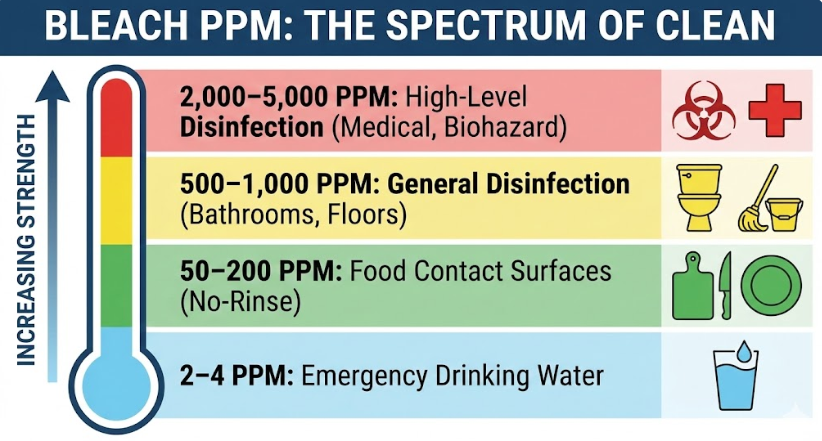
PPM stands for "parts per million." When we talk about bleach solutions, it refers to the concentration of active chlorine available to kill germs. Federal and state health agencies, like the CDC and local health departments, provide specific PPM guidelines for different applications to ensure sanitization is effective.
- 100-200 PPM: This is the standard range for sanitizing food contact surfaces, dishes, and toys. Solutions in this range kill most common bacteria without being overly corrosive.
- 500-1,000 PPM: This higher concentration is typically used for disinfecting non-porous surfaces that may have been exposed to blood or other bodily fluids.
- 5,000+ PPM: This is an industrial-strength concentration used for things like sanitizing well water after a flood or for situations involving highly resilient pathogens.
The problem is that the concentration of standard household bleach can vary, typically ranging from 5.25% to 8.25% sodium hypochlorite. This makes a simple "one cap per gallon" recipe unreliable. A Bleach PPM Calculator solves this by factoring in your specific bleach's concentration to give you a precise, volume-based recipe.
How a Bleach PPM Calculator Works: The Core Formula
The calculator uses a foundational chemistry principle called the dilution equation: C1V1=C2V2.
- C1 = Initial concentration of your bleach (e.g., 6%).
- V1 = Volume of bleach you need to add (this is what the calculator solves for).
- C2 = Desired final concentration of your solution (in PPM).
- V2 = Desired final volume of your solution (e.g., 1 gallon).
By plugging in your bleach's percentage and your target PPM, the calculator determines the exact amount of bleach you need to add to your water. This eliminates all the guesswork and ensures you're meeting official safety standards.
It’s easy to calculate parts per million without manual formulas
How to Use the Calculator: A Step-by-Step Example
- Find Your Bleach Concentration: Check the label on your bottle of plain, unscented bleach. It will list the percentage of sodium hypochlorite, often 6% or 8.25%. Input this number into the calculator.
- Choose Your Desired PPM: Based on your task, input the target PPM. For sanitizing food prep surfaces, you'd likely use 200 PPM.
- Specify Your Volume: Enter how much of the final solution you want to make, for example, 1 gallon or 1 liter.
- Get Your Results: The calculator will tell you exactly how many tablespoons, teaspoons, or milliliters of bleach you need to add.
For example, if you're making a 200 PPM solution with 6% bleach in a 1-gallon container, the calculator would tell you to add approximately 1.5 tablespoons of bleach. This is a far more accurate and reliable method than relying on generic charts.
Top Tips for Safe and Effective Bleach Sanitization
Using a calculator is just one part of the process. For optimal results and safety, remember these key practices:
- Always use plain, unscented bleach. Scented or "color-safe" bleaches contain additives that make them ineffective for sanitizing.
- Never mix bleach with other cleaners. Combining bleach with ammonia or acids (like vinegar) can create toxic, potentially lethal gases.
- Use a fresh solution daily. Bleach solutions lose their potency over time, especially when exposed to light. Mix a new batch each day you plan to use it.
- Clean first, sanitize second. A sanitizer is only effective on a clean surface. Always wash surfaces with soap and water and rinse them thoroughly before applying your bleach solution.
- Wear protective gear. Always wear gloves and eye protection when handling concentrated bleach or making a solution.
- Work in a well-ventilated area. Open windows and doors to ensure proper airflow and avoid inhaling fumes.
By using a reliable calculator and following these safety guidelines, you can be confident that your sanitizing solution is effective and that you are working safely.
