PPM ↔ Microsiemens Calculator
Convert between Total Dissolved Solids (PPM) and Electrical Conductivity (µS/cm) using an adjustable conversion factor (CF).
PPM = µS/cm × CF. CF depends on dissolved ion composition.
PPM to µS/cm Converter – Hydroponics Nutrient EC Calculator
Convert PPM to microsiemens for precise nutrient mixing. Supports 500, 640, and 700 scale conversions for hydroponic feeding schedules and EC monitoring. Accurately convert PPM values to microsiemens for water treatment, filtration systems, aquariums, and environmental testing using standard conversion factors.
How to Use a PPM to Microsiemens Calculator
Are you trying to measure the water quality for your aquarium, hydroponics system, or home water filter? Understanding the relationship between Parts Per Million (PPM) and Microsiemens (μS/cm) is essential.
Our PPM to Microsiemens Calculator is a simple tool designed to help you quickly convert these values, so you can make informed decisions about your water.
What Problem Does This Calculator Solve?
Many water quality meters, like Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) meters, output results in PPM. However, another common unit of measurement for water conductivity is Microsiemens (μS/cm), often used in scientific or commercial settings. The calculator bridges this gap by converting one measurement to the other.
This is especially useful if you have a meter that only reads in PPM but a guide or set of instructions that specifies a target conductivity in Microsiemens. It’s the perfect tool for hobbyists, farmers, and anyone who needs to accurately monitor water conditions without complex manual calculations.
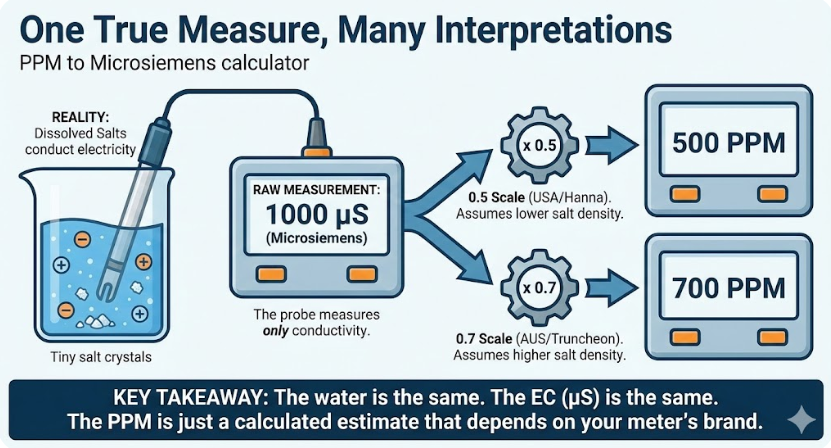
How to Calculate PPM to Microsiemens
The conversion isn’t a fixed, universal number because it depends on the type of dissolved solids in the water. This is where the TDS Factor comes in. This factor is essentially a conversion constant that accounts for the specific salts and minerals present.
To use our calculator, you will need two pieces of information:
- PPM Value: This is the reading from your TDS meter.
- TDS Factor: This is the conversion constant. For most common water sources (e.g., tap water, nutrient solutions), a factor between 0.5 and 0.7 is standard. A common industry-standard TDS factor is 0.67, which is a great starting point if you’re unsure.
Once you have these two values, the calculation is straightforward: PPM×TDS Factor=Microsiemens (μS/cm)
For example, if your TDS meter reads 300 PPM and you use a TDS Factor of 0.67, the calculation would be: 300×0.67=201μS/cm
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- “What is the difference between PPM and Microsiemens?”PPM (Parts Per Million) measures the mass of dissolved solids in the water. Microsiemens (μS/cm) measures the water’s electrical conductivity. While both are indicators of water purity, they represent different physical properties.
- “Why do I need a TDS Factor?”The TDS Factor is crucial because a PPM reading is an estimate. Different types of dissolved solids conduct electricity differently. The factor calibrates the conversion for the specific water you are testing. Without it, the conversion would be inaccurate.
- “What TDS Factor should I use?”The ideal factor depends on your meter’s calibration and the water’s source. Most meters are calibrated to a specific factor, often 0.5 or 0.7. If your manual doesn’t specify, using a common factor like 0.67 is a reliable choice for general purposes. You can experiment with different factors to see which one best matches your other water test results.
Using a dedicated calculator ensures accuracy and saves you the time of manual conversions. With just a few clicks, you can get the precise Microsiemens value you need for any application, from growing healthy plants to maintaining your freshwater aquarium.
